If you’ve ever held a marshmallow between your fingers — soft, white, impossibly light — and wondered what’s actually inside it, you’re not alone. That fluffy texture seems almost too good to be natural. And honestly? The answer is surprisingly simple, but the process behind it is more fascinating than most people realize.
This guide walks you through every stage: the raw ingredients, what happens inside a factory, how quality is controlled, and where the marshmallow industry is heading in the years ahead.
What Is a Marshmallow, Really?
Before diving into the “how,” it helps to know the “what.” A marshmallow is, at its core, an aerated candy foam — a structure where millions of tiny air bubbles are suspended in a sugary gelatin matrix. That’s what creates that distinctive springy bite that collapses softly in your mouth.[cen.acs]
The modern marshmallow bears almost no resemblance to its ancient ancestor. Originally, marshmallow candy was derived from the root sap of the marsh mallow plant (Althaea officinalis), a flowering herb used medicinally in ancient Egypt to soothe sore throats and treat wounds. It was combined with honey and egg white to form a dense, medicinal paste — not the fluffy pillow candy we know today.[britannica]
By the late 19th century, French confectioners had replaced mallow root sap with gelatin, which was more stable, more consistent, and infinitely easier to source at industrial scale. American candy manufacturers later mechanized the process entirely, turning what had been a slow, handmade specialty into a mass-produced staple found in every grocery store.[anec]
The Core Ingredients: Simple, But Precisely Balanced
Modern marshmallow production requires surprisingly few raw ingredients. What matters isn’t the ingredient list — it’s the ratio.
| Ingrediente | Role in the Marshmallow | Typical Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| Sucrose (Sugar) | Provides sweetness and structural bulk | ~30% of dry weight |
| Corn Syrup (Glucose) | Prevents sugar crystallization; maintains softness | ~60% of sugar mixture |
| Gelatina | Forms the foam scaffold; gives stretch and chew | 1–2% |
| Agua | Dissolves sugar; activates gelatin; carriers for flavors | Variable |
| Egg Albumen or Soy Protein | Assists foam formation and stability | Optional |
| Flavoring & Colorants | Taste and visual appeal | Trace amounts |
wikipedia+2
A key detail that many people overlook: the corn syrup-to-sugar ratio is deliberately engineered to keep sugar molecules in a disordered, amorphous state. If sucrose were allowed to crystallize, the marshmallow would turn grainy and hard. The glucose in corn syrup disrupts that crystallization, locking in the smooth, melt-in-mouth texture that consumers expect.[en.wikipedia]
“A marshmallow is basically a foam that’s stabilized by gelatin,” says Richard Hartel, a food engineer at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. That sentence sounds simple. In practice, achieving that foam at consistent industrial scale is a feat of food engineering.[cen.acs]
Step-by-Step: How a Marshmallow Is Made in a Factory
Walk through any major marshmallow production facility, and you’ll see the same core process, even if the machines differ by manufacturer. Here’s the full sequence:
Step 1 — Ingredient Preparation
Everything begins with sourcing and checking raw materials. Gelatin is bloomed — soaked in cold water for several hours until it fully absorbs the liquid and swells into a soft gel. Meanwhile, sucrose, glucose syrup, and water are weighed and combined in a cooking vessel. Quality teams verify the grade and purity of each input through HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) testing before any batch moves forward.sinofudetechnology+1
Step 2 — Cooking the Sugar Syrup
The sugar-syrup mixture is heated — carefully and precisely — to approximately 240°F (115°C), a temperature known in confectionery science as the “soft-ball stage”. This is not a detail you can guess at. Too low, and the marshmallow won’t set. Too high, and it turns brittle. Industrial operations use automated thermometers and pressure sensors to monitor this in real time.sinofudetechnology+1
Step 3 — Combining Gelatin and Syrup
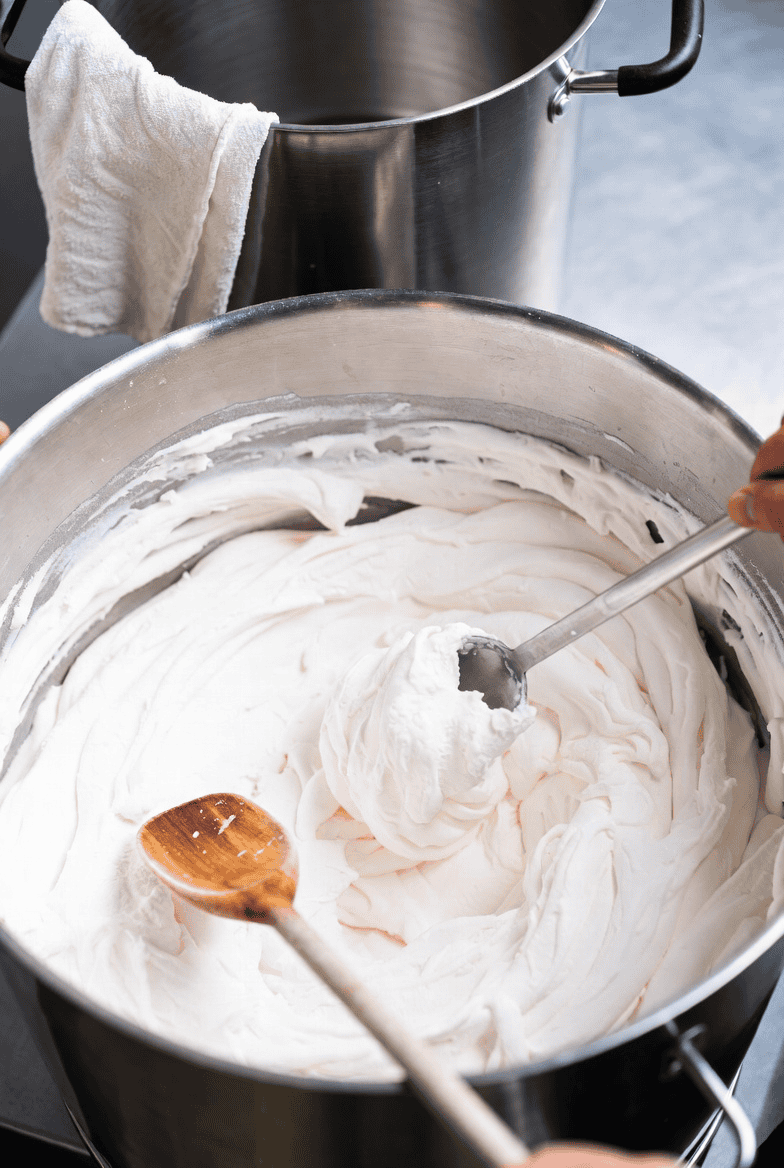
Once the syrup hits temperature, it’s removed from heat and allowed to cool slightly. The bloomed gelatin is then introduced into the warm syrup with continuous stirring at low speed. This stage matters enormously: if you add gelatin to syrup that’s still too hot, the protein structure denatures and you lose the foam-forming capability. The mixture must be warm enough to stay fluid, but not so hot it destroys the gelatin.[sinofudetechnology]
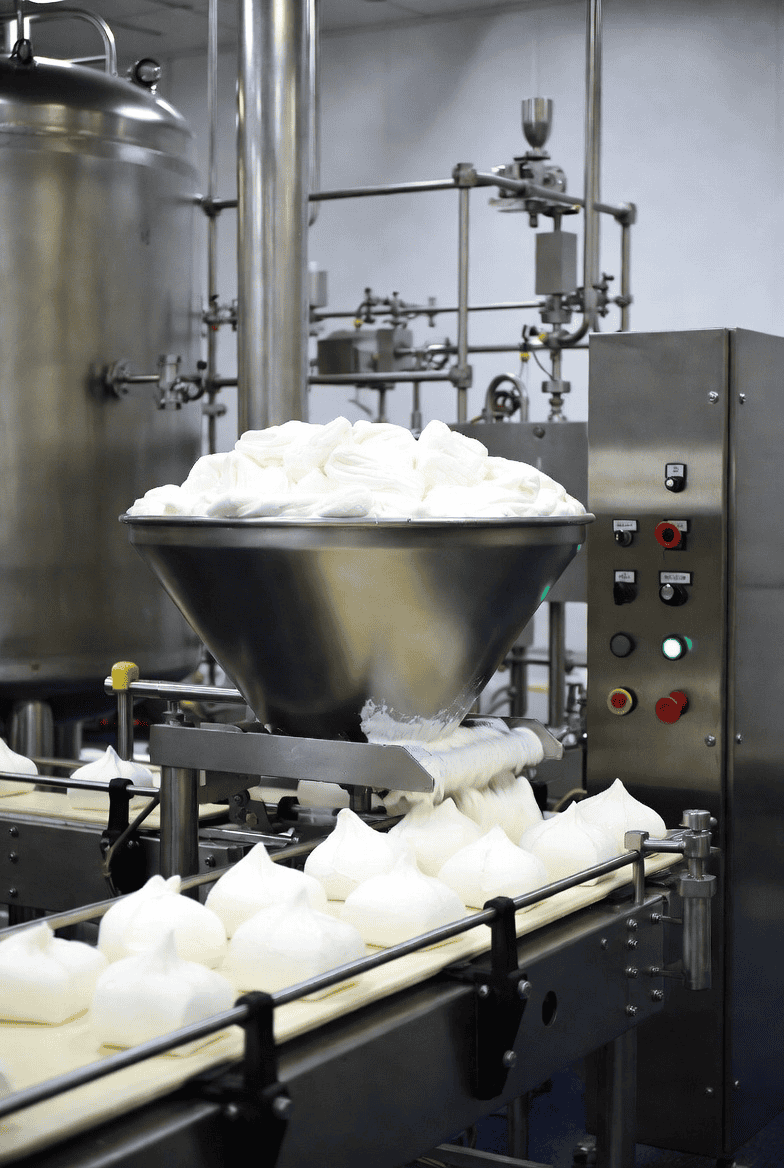
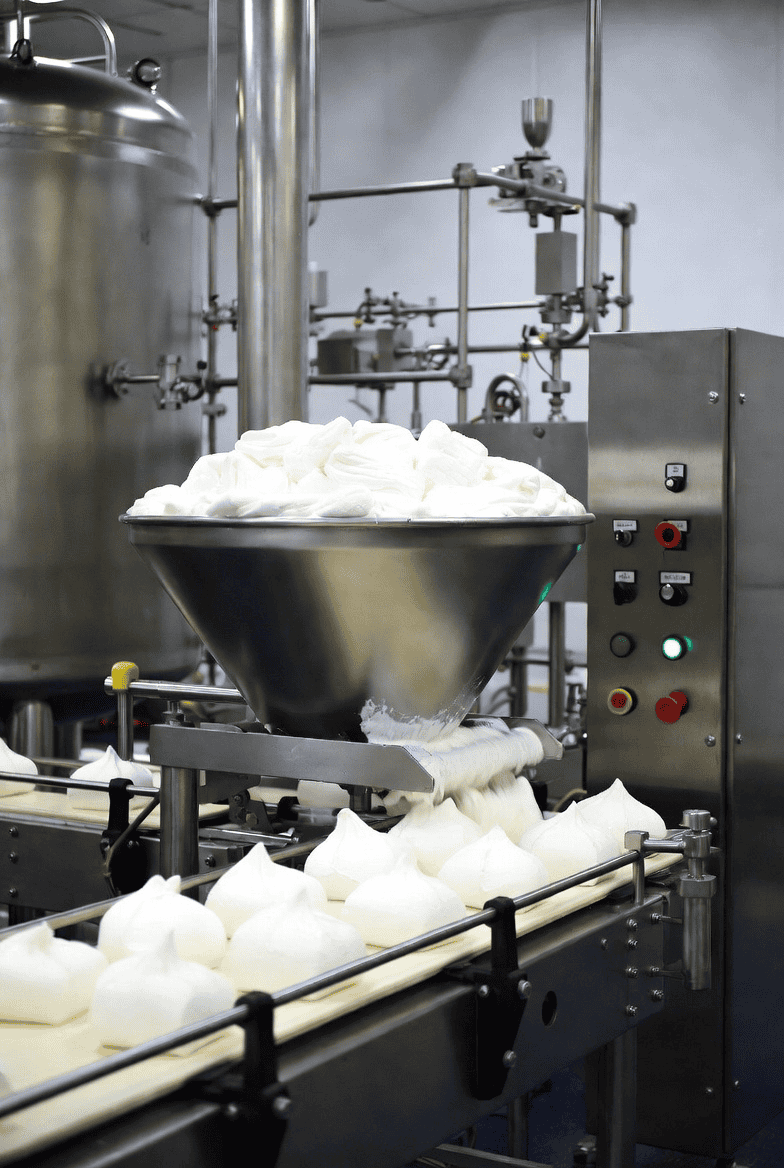
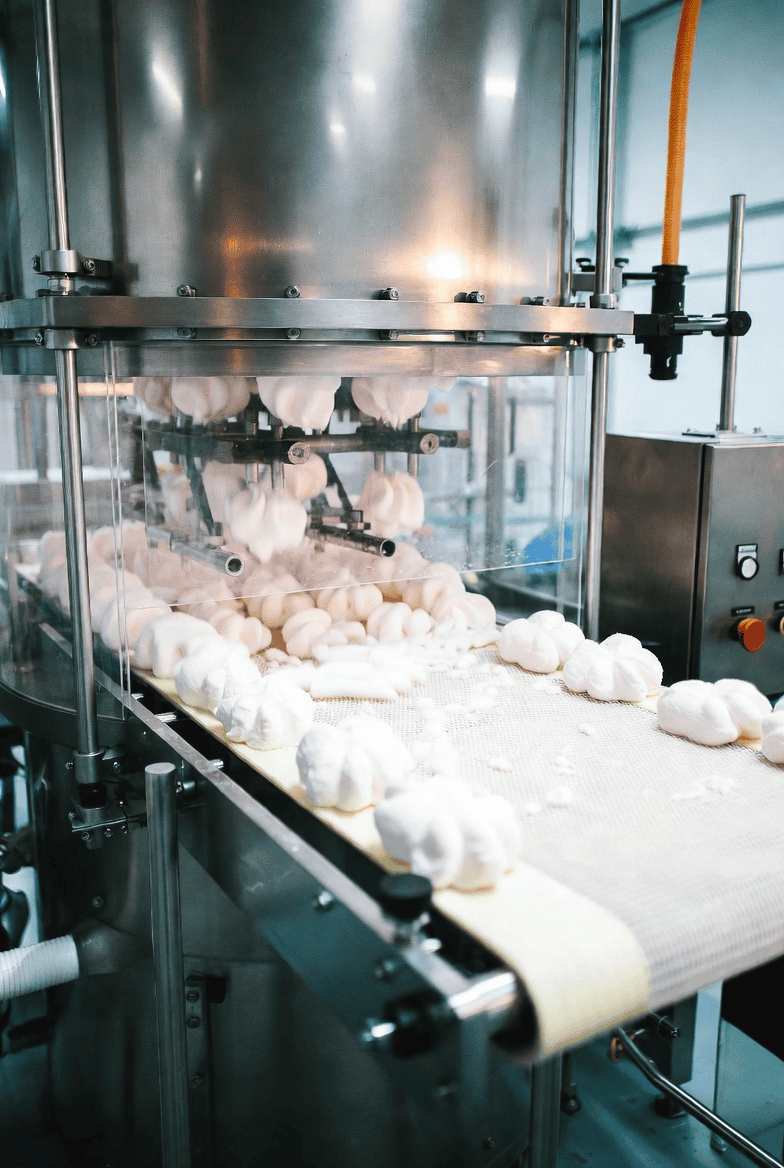
Step 4 — Aeration (The Critical Step)
This is where the magic happens. The gelatin-syrup mixture is transferred to a high-speed industrial aerator — a rotor-stator device where pins on a rotating cylinder intermesh with stationary pins on the wall. Compressed air is injected into the warm mixture as the machine whips at high speed, breaking large air bubbles into millions of tiny, uniform ones.[en.wikipedia]
Why does this matter? The fineness and uniformity of the air cells directly determine the smoothness of the final marshmallow. A coarser foam gives a grainy or uneven texture. Factory-grade aerators can achieve bubble diameters in the range of micrometers — consistently, batch after batch.[lechaocandy]
This whipping process typically runs for 10–15 minutes. Temperature during aeration must be held just above the melting point of gelatin, ensuring the mixture stays fluid enough to incorporate air while the gelatin begins forming its network.[sinofudetechnology]
Step 5 — Forming and Shaping
Once aerated to the right volume and consistency, the marshmallow mass is shaped. There are two main methods used in modern factories:
-
Extrusion: The foam is pushed through nozzles in a continuous rope or ribbon, which is later cut into segments. This is the method used for standard pillow-shaped marshmallows and twisted varieties.[gondormachinery]
-
Starch Mogul Depositing: A tray of cornstarch has shapes pressed into it, creating cavities. The foam mixture is deposited into those cavities and allowed to cool and set within the starch. This technique is used for novelty shapes — seasonal items, animals, and specialty designs.[anec]
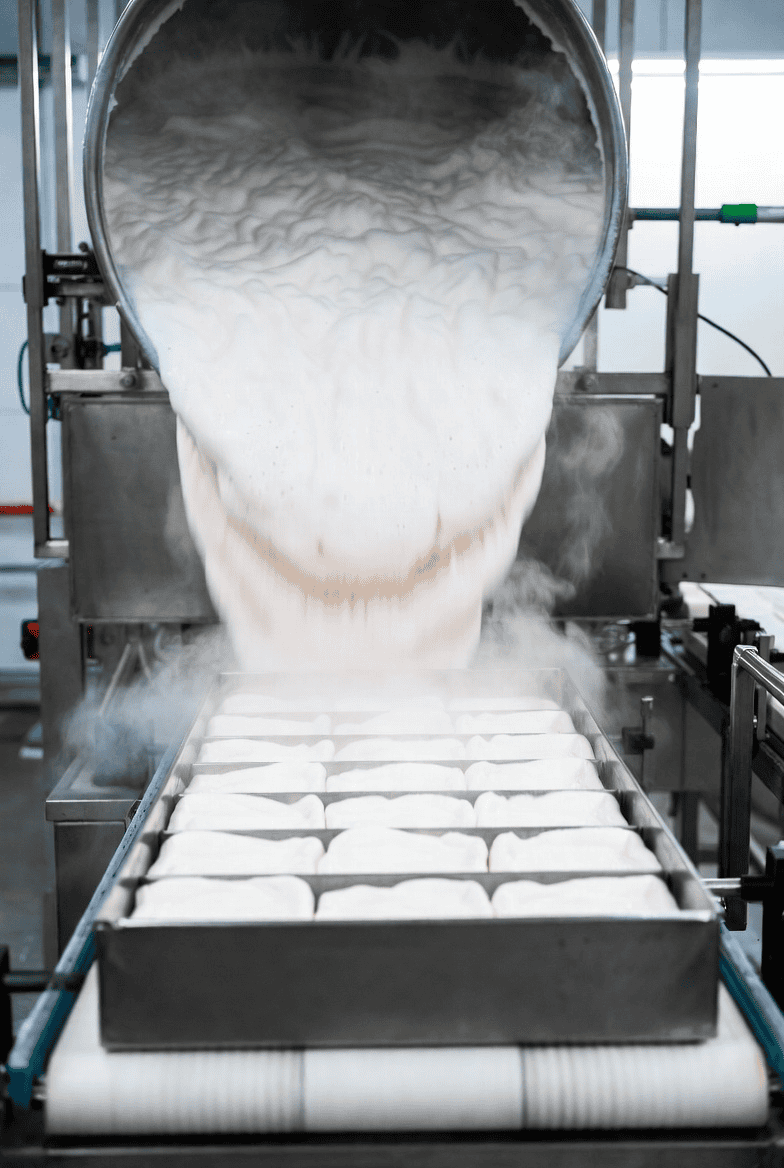
Step 6 — Cooling and Setting
Shaped marshmallows travel through a tunel de enfriamiento, a controlled environment where temperature and humidity are precisely managed to allow the gelatin network to fully set. Rush this step, and marshmallows won’t hold their shape. The cooling stage also determines final moisture content — studies indicate the water content must stay between 15–18% for optimal texture: not sticky, not dry.sinofudetechnology+1
Step 7 — Coating and Anti-Stick Treatment
After cooling, marshmallows are tumbled in a light coating of powdered sugar, cornstarch, or a combination of both. This is purely functional — it prevents individual pieces from sticking together during packaging and extends shelf life by limiting surface moisture absorption.[sinofudetechnology]
Step 8 — Quality Control
Before any marshmallow ships, it passes through a battery of checks. Texture analyzers measure elasticity and density. Moisture meters verify water content. Sensory panels assess aroma, color uniformity, and taste. Factories operating under HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) standards run microbiological tests on production samples throughout the day.[sinofudetechnology]
Step 9 — Packaging
The final step: weighing, sealing, and labeling. Automated packaging machines portion marshmallows into bags, heat-seal them under modified atmosphere conditions (to extend shelf life), and apply labels. From raw gelatin to sealed bag, the entire process in a modern facility can take under 90 minutes per batch.
Factory vs. Homemade: What’s the Real Difference?
This is a question worth answering honestly, because the internet is full of oversimplified comparisons.
| Factor | Factory-Made | Homemade |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredientes | Corn syrup, sugar, gelatin, stabilizers, artificial or natural flavors | Sugar, gelatin, water, egg whites; natural flavors optional |
| Textura | Highly consistent; engineered for shelf stability | Softer, fresher; more variable |
| Shelf Life | 6–12 months (treated and sealed) | 2–3 weeks at room temperature |
| Personalización | Limited to product lines | Full control over flavor, color, shape |
| Aeration Quality | Extremely fine, uniform bubbles via industrial aerator | Coarser bubbles via stand mixer |
| Conservantes | Often includes stabilizers and moisture controllers | Typically none |
The honest answer: homemade marshmallows taste different — not necessarily better or worse, but fresher and more fragile. Factory marshmallows are engineered for logistics, not just taste. That’s not a criticism; it’s a design decision that makes a shelf-stable snack available year-round at scale.
Industry Applications Beyond the Campfire
Most people associate marshmallows with hot cocoa and s’mores. The actual industrial application range is much wider — and growing.
Food & Beverage Manufacturing
-
Baking and pastry: Marshmallow cream is used in frosting, fillings, and cake layers
-
Confectionery production: Marshmallows serve as structural or flavor components in chocolate-enrobed candy bars, nougat-adjacent products, and layered confections
-
Cereal and snack foods: Commercially produced cereals like Lucky Charms use dehydrated marshmallow bits — a whole separate sub-process involving freeze-drying or hot-air drying
Foodservice and Hospitality
-
Specialty dessert menus increasingly feature toasted marshmallow elements — torched tableside or pre-infused with flavors like bourbon, lavender, and cardamom[sinofudetechnology]
-
Hot cocoa and specialty coffee bars use artisan marshmallows as a premium add-on
Health and Wellness (Niche)
-
The original marshmallow plant root was a soothing agent for throat irritation, and the tradition persists in herbal medicine formulations
-
Soft marshmallow texture has been explored in the context of dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) management in clinical nutrition
Craft and DIY
-
Marshmallows are used in children’s crafts, architectural modeling projects (the classic “spaghetti bridge” activity), and even artisan candle-making[gondormachinery]
The Future of Marshmallow Production
The marshmallow market isn’t standing still. Several trends are actively reshaping how marshmallows are made, marketed, and consumed.
Market Growth is Substantial
The global marshmallow market was valued at $3.5 billion USD in 2024 and is projected to reach $5.8 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.0%. The global marshmallow production equipment market alone — the machinery used to make them — was valued at $415 million in 2024, expected to reach $722 million by 2033 at a CAGR of 6.3%.marketintelo+1
Plant-Based and Vegan Formulations
Traditional marshmallows rely on animal-derived gelatin. The fastest-growing innovation segment is replacing gelatin with plant-based alternatives: carrageenan (from seaweed), agar-agar, pectin, and modified starches. Brands like Dandies have already built substantial market presence on vegan marshmallows. Industrial formulators are also experimenting with guar gum and pectin combinations to replicate gelatin’s foam stability in vegan-friendly compositions.verifiedmarketreports
Clean-Label Demand
Consumers are reading ingredient lists more carefully than ever. The industry response has been a shift toward natural colorants (beet-derived red, spirulina green, turmeric yellow) and natural flavor extracts. Emulsifiers are shifting from synthetic polysorbates to sunflower lecithin and soy lecithin, which carry more favorable consumer perception.[sinofudetechnology]
Ingredientes funcionales
Research teams are incorporating functional components into marshmallow matrices: multicomponent fruit and vegetable pastes, chia seeds, and adaptogenic ingredients. A notable 2021 study found that replacing 75% of apple puree in marshmallow formulations with a multicomponent fruit-vegetable paste improved viscosity and organoleptic properties while increasing nutritional value.journals.uran+1
Automation and Precision Manufacturing
Asia-Pacific is projected to grow at the highest CAGR of 7.8% in marshmallow production equipment, driven by expanding confectionery manufacturing in China, India, and Southeast Asia. The equipment evolution is toward automated vacuum whipping systems that control both temperature and gas injection ratio simultaneously, reducing batch variance and product waste.marketintelo+1
| Future Trend | Qué lo impulsa | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Vegan gelatin alternatives | Plant-based consumer demand; ethics | Active now, scaling 2025–2027 |
| Functional ingredient integration | Health-conscious snacking | R&D phase; commercial launch emerging |
| Clean-label formulation | Label transparency demand | Active now across major brands |
| AI-assisted production monitoring | Quality consistency; labor costs | Pilot programs in advanced facilities |
| Sustainable packaging | ESG commitments; regulatory pressure | 2025–2028 regulatory push |
verifiedmarketreports+2
FAQ: Real Questions About How Marshmallows Are Made
Q: Is gelatin the only thing that makes marshmallows fluffy?
No — gelatin stabilizes the foam, but the fluffiness itself comes from the aeration process. Without vigorous whipping that introduces air, you’d have a dense, gummy mass even with perfect gelatin.[cen.acs]
Q: What temperature does the sugar syrup need to reach?
The syrup must hit approximately 240°F (115°C), the “soft-ball stage” in candy making. This ensures the right concentration and structure for the final foam.britannica+1
Q: Why are marshmallows coated in cornstarch or powdered sugar?
It’s purely anti-stick. Without this coating, marshmallows fuse together during storage and handling. The coating absorbs surface moisture and keeps each piece separate.[sinofudetechnology]
Q: Can you make marshmallows without gelatin?
Yes — vegan marshmallows use carrageenan, agar-agar, or modified starch as substitutes. The texture differs slightly (often slightly firmer or less stretchy), but the result is fully functional and commercially viable. Dandies and several other brands have proven this at scale.[verifiedmarketreports]
Q: How long does industrial marshmallow production take?
From raw ingredients to packaged product, a modern automated facility can complete the cycle in under 90 minutes per batch. Homemade marshmallows generally require 2–4 hours including bloom time and setting.sinofudetechnology+1
Q: Why do marshmallows brown when roasted?
That’s the Maillard reaction — the same chemical process that browns bread and sears meat. The surface sugars and amino acids react under heat, creating complex flavor compounds and that golden-brown crust. The center simultaneously heats and softens as the gelatin structure partially breaks down.[en.wikipedia]
Recommended: Industrial Marshmallow Production Equipment
If you’re exploring marshmallow manufacturing at a commercial scale, these are the core production line components worth evaluating:
-
Sinofude Technology Marshmallow Production Line — Full automated line covering mixing, aeration, forming, and cooling: sinofudetechnology.com
-
Gondor Machinery Marshmallow Making Machines — Modular equipment for mid-scale operations, with extrusion and depositor configurations: gondormachinery.com
Authoritative External References
For further reading and source verification, these high-authority sources were referenced in building this guide:
-
Britannica — Marshmallow History and Preparation (DA 90+): britannica.com/topic/marshmallow
-
Wikipedia — Marshmallow (Food Science & Composition) (DA 90+): en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marshmallow
-
Chemical & Engineering News (ACS) — Marshmallow Ingredients Chemistry (DA 75+): cen.acs.org
-
Verified Market Reports — Global Marshmallow Market Size 2024–2033 (DA 55+): verifiedmarketreports.com
-
Market Intelligence — Marshmallow Production Equipment Market 2033 (DA 50+): marketintelo.com
This is how a marshmallow is made — from a bog plant used in Egyptian medicine to a precisely engineered foam produced at industrial scale across six continents. The ingredients are four. The chemistry behind them is anything but simple.britannica+2