Interested in learning how flavored boba is made? In this article, you’ll learn the science behind the Spherification process, the ingredients, and the storage life of flavored boba. We’ll also discuss the benefits of flavored boba for health and wellness. Besides being tasty, these tasty treats are also low-calorie and fun. Plus, they come in convenient packs and are ready to serve.
Spherification process of flavored boba
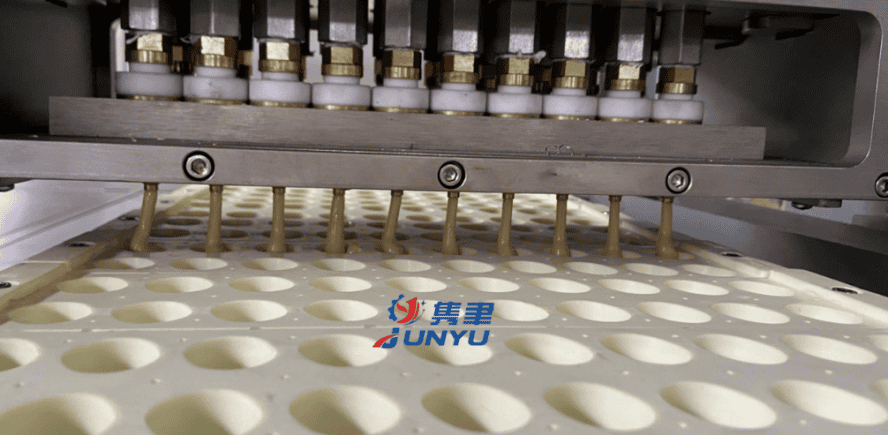
The spherification process of juice coating on popping boba is based on the principles of molecular gastronomy, which focuses on the physical and chemical changes in food. Sodium alginate, a polysaccharide, is combined with calcium chloride in a solution. The result is a gel-like outer covering. The process of spherification is similar to the way water drops are coated in vegetable oil.
The process of spherification uses calcium chloride and alginate, two chemical compounds that combine to form a gel when mixed with water. It is commonly used to make bursting boba in bubble tea, and is also used in the production of ravioli and caviar. In the food industry, agar is another popular material used for spherification. It is inexpensive and widely available.
Ingredients
Creating a delicious pop-your-boba snack is as easy as following a few simple steps. Start by preparing your liquid ingredients. You’ll need 4 main ingredients: calcium salt, sodium alginate, and fruit juice. Once you’ve prepared all of them, it’s time to mix them up. Once they’ve been mixed together, the resulting mixture should form a solid ball that will sink to the bottom. Next, you’ll need a syringe or squeeze bottle to release the juice and alginate mix. Use the same technique as for making ice cream or instant noodles.
Popping boba is similar to the tapioca bobas used in bubble tea, with a thin membrane surrounding the juice and bursting when put in your mouth. Just like tapioca boba, popping boba is made from a fruit juice that’s spherified with a chemical process known as spherification. Sodium alginate is processed by adding calcium chloride, which turns it into a gel and forms the outer wall of the pop-your-boba.
Science behind spherification process
Spherification is the process by which chefs produce popping boba, a Japanese candy that has a thin gel-like skin on the outside and a sweet juice inside. To create them, chefs add sodium alginate to a mixture of juice and water, then drop it into a calcium chloride bath. The addition of calcium replaces sodium ions in the solution and links polymer chains together, preventing them from separating and letting the liquid inside.
To create boba, you can use a caviar maker or a spherification kit. First, make a solution of sodium alginate with 100ml of juice. Then, add a bit more than the recommended amount, but this won’t affect the boba too much. Also, remember that smaller spheres are harder to sink into a thick solution because of surface tension. If the spheres are longer, the gel will be thicker, but smaller ones won’t.
Storage life
The storage life of juice-coated popping boba is not as long as that of other frozen treats. But if you have a hard time finding a good supplier of frozen desserts, you can try making your own at home. Popping boba is a popular dessert that has been popular in Japan for decades. The ingredients used to make this dessert are tapioca flour, juice, and fruit juices.
To make the poppable bubbles, you will need a sphere mould. The spheres contain the juice and will pop when sucked up through a chunky straw. Once popped, the balls can be stored for up to 24 hours. To preserve their freshness, you should consume them within a day or two after opening. You can also keep them in the refrigerator for longer storage.
Health benefits of boba
Popping boba has become popular in Westernized countries, and many people wonder what the health benefits are. Fortunately, there are plenty of reasons to consider juice-coated boba. The tasty treat is not only refreshing, but it’s also good for your body. Read on to discover more. This simple recipe is made with sodium alginate and calcium lactate, two ingredients with proven health benefits. Sodium alginate improves bubble formation and is used by many food manufacturers as a preservative. Sodium alginate, which is an excellent source of calcium, is commonly used to improve the flavor and shelf life of food products. It’s also used in soft drinks because it adds a softer membrane.
While traditional boba is made of tapioca, juice-coated boba is filled with fruit juice. Sodium alginate undergoes a chemical reaction called spherification, which creates an outer gel layer around the juice. The process results in a softer, more palatable snack that’s perfect for adding to frozen yogurt and fruity bubble tea. The added fruit juice enhances the taste of these sweet treats.